Heatmap - Closest Average
The Heatmap - Closest Average indicator produces a color-coded map visualizing the average travel time to points, such as POIs, from surrounding areas.
1. Explanation
The heatmap displays a color-coded hexagonal grid showing average travel times to destinations (opportunities) using real-world transport networks. You can specify the routing type, opportunity layer, number of destinations and travel time limit to generate the visualization.
The Opportunity layer contains point-based destination data (POIs, transit stations, schools, amenities, or custom data) that you want to analyze accessibility to. You can use multiple opportunity layers and they will be combined into a unified heatmap.
The Number of destinations sets the calculation of average travel time to only the n closest opportunities. This creates more targeted accessibility analysis.
Key difference: Heatmaps show access from many origins to specific destinations, while catchment areas show reach from specific origins to many destinations.
Heatmaps are available in certain regions. Upon selecting a Routing type, a geofence will be displayed on the map to highlight supported regions.
If you would like to perform analyses beyond this geofence, feel free to contact us. We would be happy to discuss further options.
2. Example use cases
Do residents in certain areas have longer average travel times to amenities than others?
How does the average travel time to amenities vary across different modes of transport?
How does the average travel time vary across different types of amenities?
If standards require that a minimum number of amenities be accessible within a certain travel time, which areas meet these standards?
3. How to use the indicator?
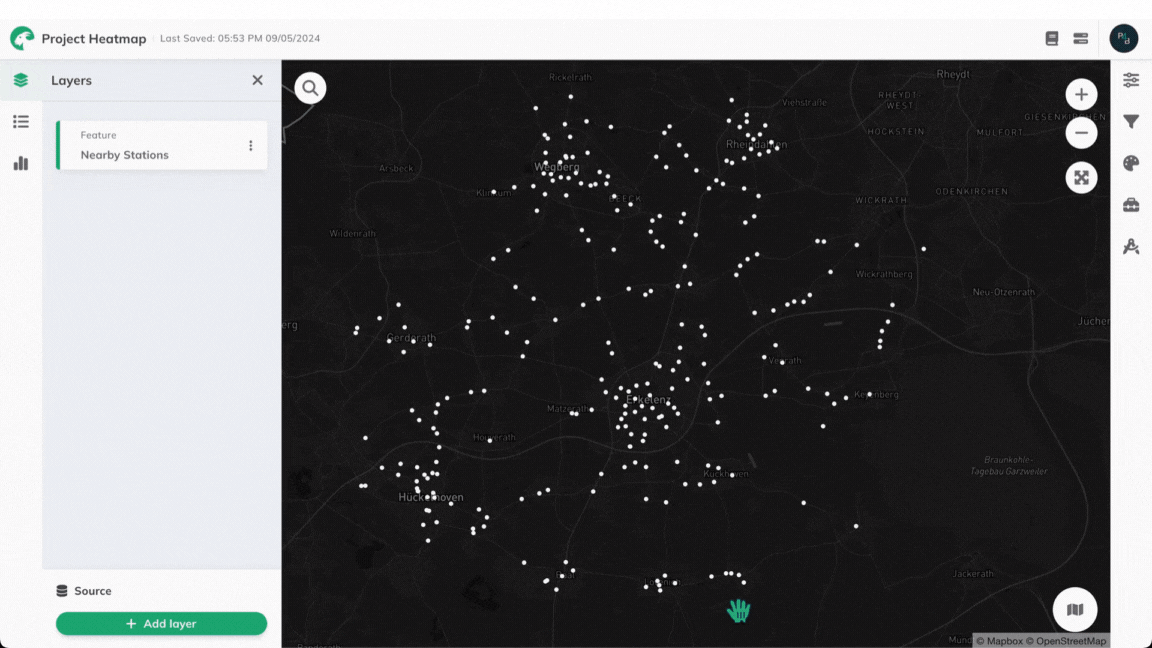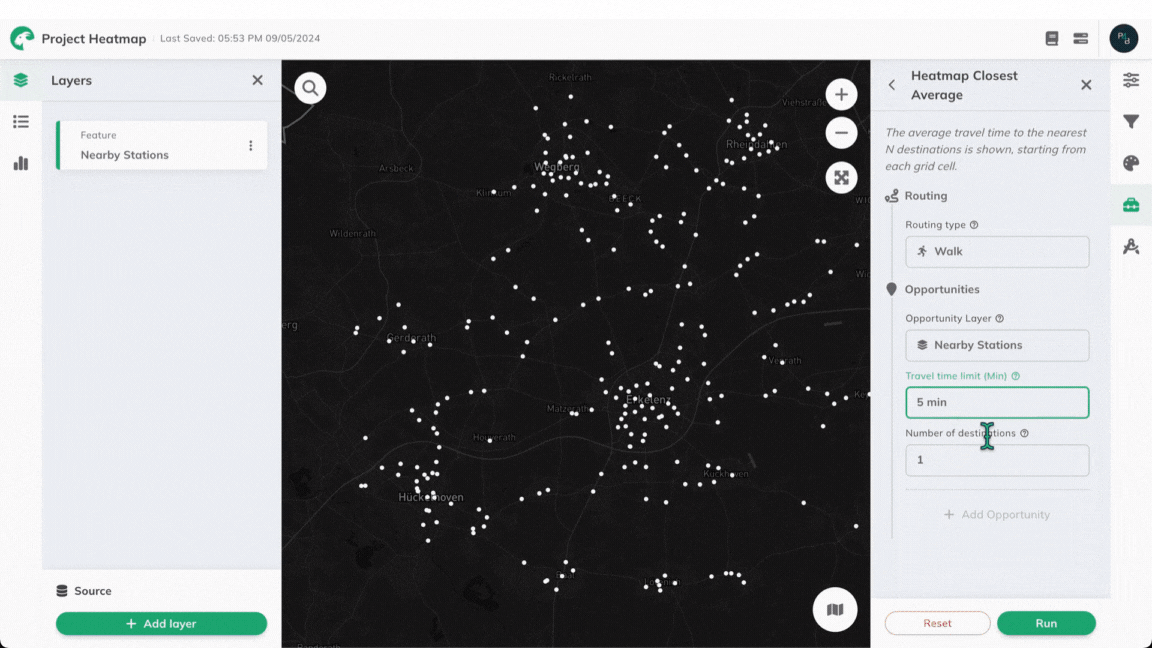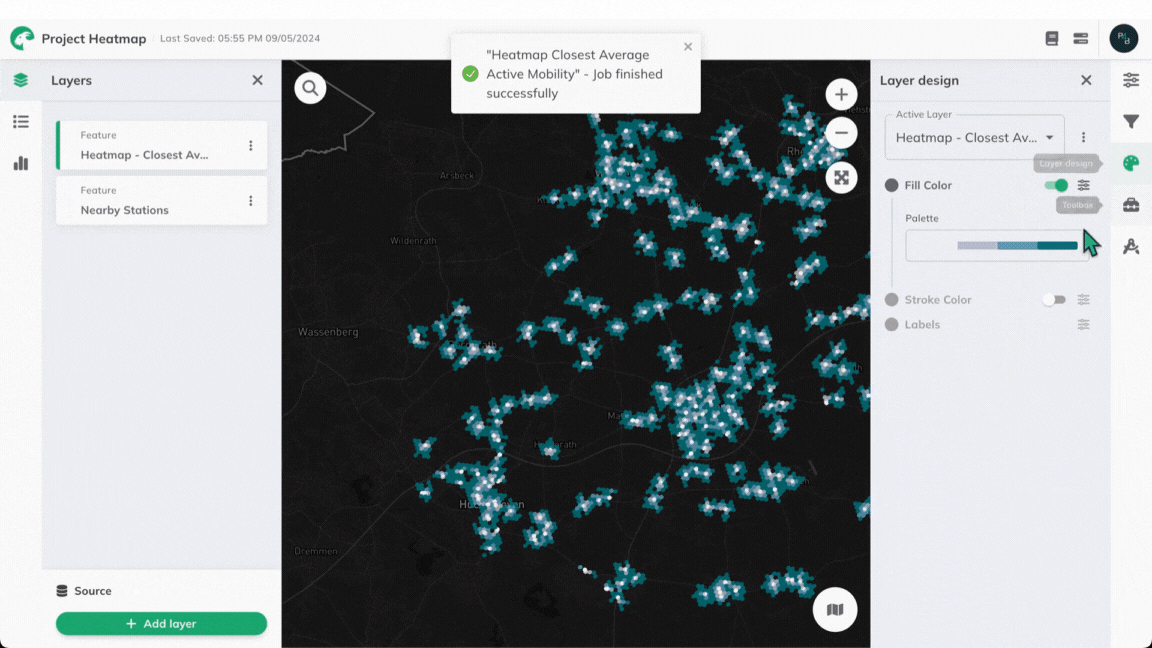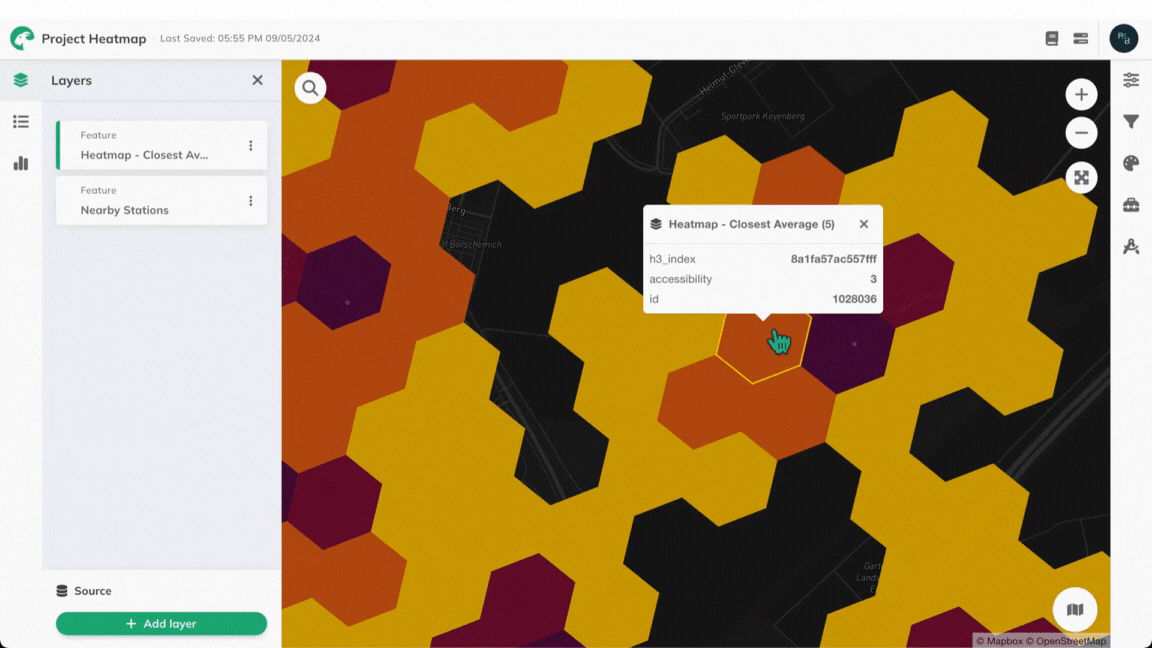
Toolbox Accessibility Indicators menu, click on Heatmap Closest Average.Routing
Routing Type you would like to use for the heatmap.- Walk
- Bicycle
- Pedelec
- Car
Walk
Considers all paths accessible by foot. For heatmaps, a walking speed of 5 km/h is assumed.
Considers all paths accessible by bicycle. This routing mode takes into account the surface, smoothness and slope of streets while computing accessibility. For heatmaps, a cycling speed of 15 km/h is assumed.
Considers all paths accessible by pedelec. This routing mode takes into account the surface and smoothness of streets while computing accessibility. For heatmaps, a pedelec speed of 23 km/h is assumed.
Considers all paths accessible by car. This routing mode takes into account speed limits and one-way access restrictions while computing accessibility.
Opportunities
Opportunity Layer from the drop-down menu. This can be any previously created layer containing point-based data.Travel Time Limit for your heatmap. This will be used in the context of your previously selected Routing Type.Need help choosing a suitable travel time limit for various common amenities? The "Standort-Werkzeug" of the City of Chemnitz can provide helpful guidance.
Number of destinations which should be considered while computing the average travel time.+ Add Opportunity to include additional point layers. Each layer can have different travel time limits and destination counts for multi-criteria analysis.Run to start the calculation of the heatmap.Results
Once the calculation is complete, a result layer will be added to the map. Clicking on any of the heatmap's hexagonal cells will reveal the computed average travel time value for this cell.
4. Technical details
Calculation
After combining all opportunity layers (for example, schools, shops, or parks), the tool creates a grid made of hexagonal cells around the area. It only includes cells where at least one opportunity can be reached based on the selected routing type (e.g., walking, cycling) and travel time limit (e.g., 15 minutes).
Then, for each cell, it calculates the average travel time to the nearest n destinations (as set in the settings).
The formula for average travel time is:
For each cell (i), the tool adds up the travel times (tij) to all reachable opportunities (j), up to n of them, and divides by n to get the average travel time.
Classification
In order to classify the accessibility levels that were computed for each grid cell, a classification based on quantiles is used by default. However, various other classification methods may be used instead. Read more in the Data Classification Methods section of the Attribute-based Styling page.
Visualization
Heatmaps in GOAT utilize Uber's H3 grid-based solution for efficient computation and easy-to-understand visualization. Behind the scenes, a pre-computed travel time matrix for each routing type utilizes this solution and is queried and further processed in real-time to compute accessibility and produce a final heatmap.
The resolution and dimensions of the hexagonal grid used depend on the selected routing type:
- Walk
- Bicycle
- Pedelec
- Car
For further insights into the Routing algorithm, visit Routing. In addition, you can check this Publication.
Example of calculation
The following examples illustrate the computation of a closest-average-based heatmap for the same opportunities, with a varying Number of destinations value.
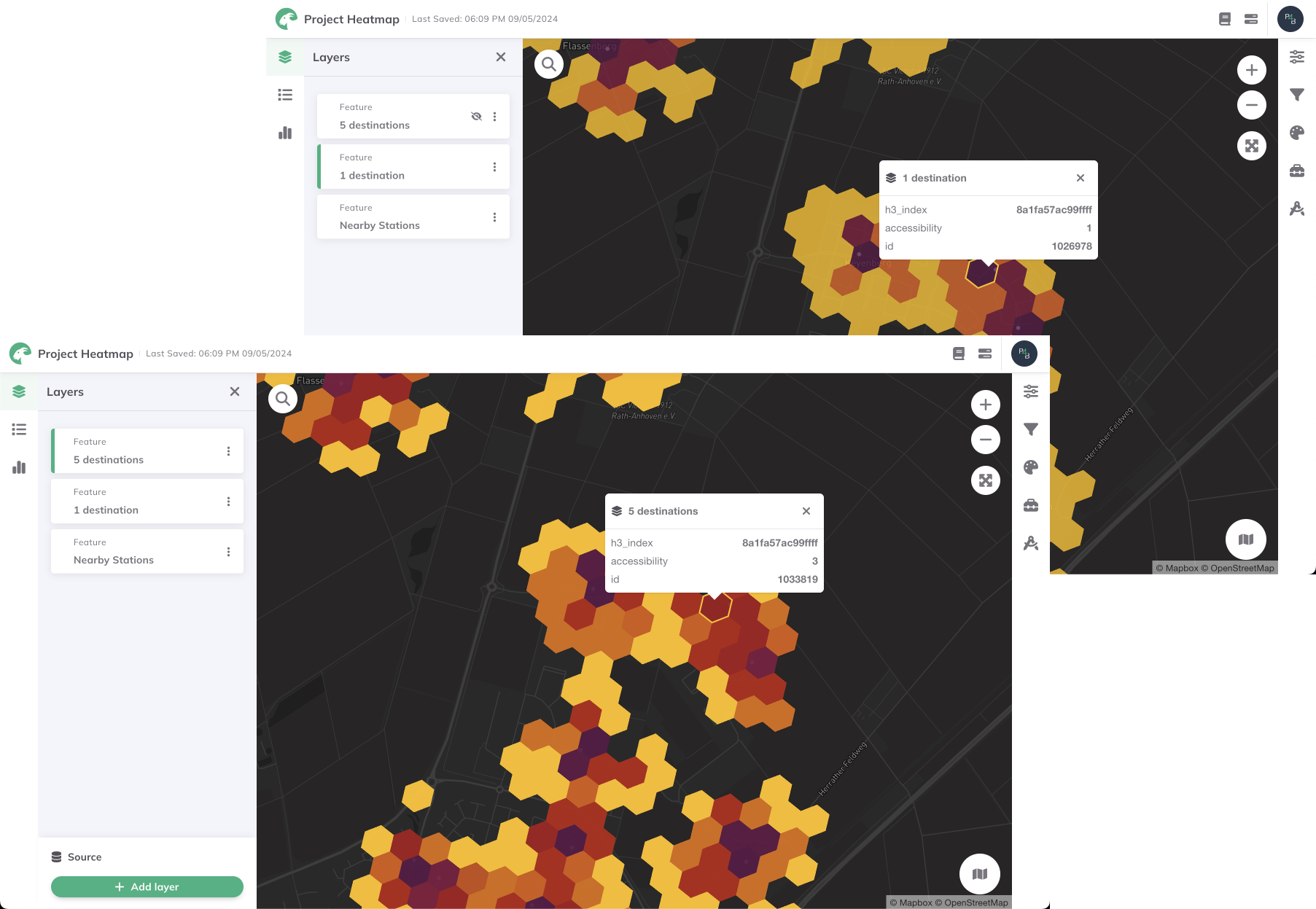
In the first example, the average travel time is computed considering only the closest destination, while in the second example, the closest 5 destinations are considered.